Lung Cancer Types, Causes, and Symptoms
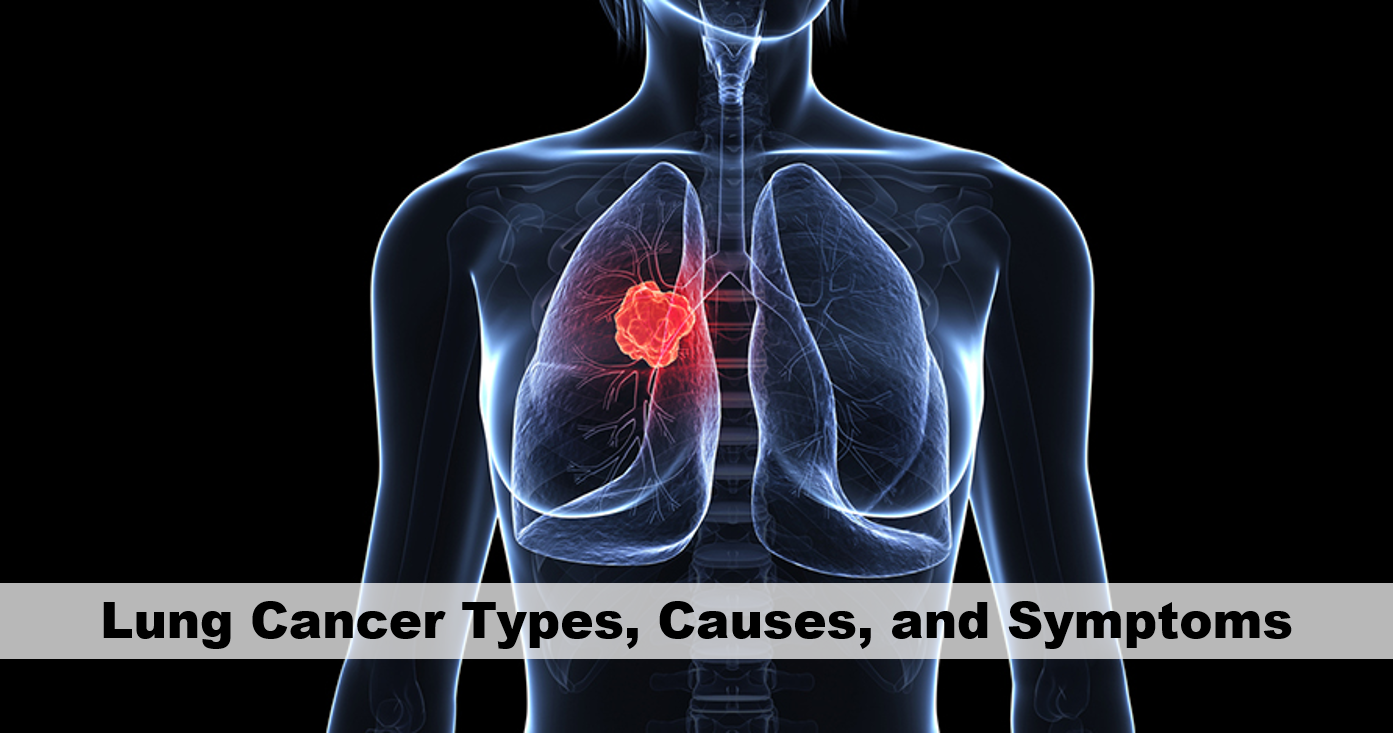
Lung Cancer Types, Causes, and Symptoms. Lung cancer is a common and dangerous cancer in the world, and it is the leading cause of death in both sexes. Lung cancer does not give early symptoms like other types of cancer, but it can be diagnosed in the early period by considering the small changes in the body. Recognizing the symptoms and avoiding smoking, the most important cause of lung cancer plays a huge role in the fight against lung cancer. Age also is an essential factor in lung cancer. Here, we will talk about lung cancer types, causes, symptoms, and treatment in the following text.
Lung Cancer Types
The lung is the organ that provides oxygen to our body. Like every organ, our lung is also made up of many cells, and these cells divide and multiply according to the need for the lung to function normally. Lung cancer is the formation of a tumor (tumor) within the lung by the proliferation of cells that are structurally normal lung tissue. Cancer cells here grow and surround the tissue, then it starts to invade the other organs and cause damage in the next stages. This spread is called metastasis. So, what are the types of lung cancer? It is divided into two main groups representing different cell types and requiring different treatment. There are separate treatment methods for both groups:
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
Small cell lung cancer is a type of cancer that progresses more rapidly and often has distant metastases when diagnosed. 85% of the patients have non-small cell lung cancer, and 15% have small cell cancer.
Lung Cancer Causes
- Cigarette, cigar, pipe (tobacco) smoking
- Tuberculosis
- Having had lung cancer before. There is a risk of developing cancer again in patients who have undergone surgery for lung cancer or have received radiation therapy. Smoking also increases this risk.
- Asbestos: Used in mines, ships, insulation materials. Causes long-term problem in the respiratory tract.
- Radon: It is an odorless radioactive gas that is naturally found in soil and homes.
- Uranium ore
- Inhaled substance or object / Gas and Chemical Exposure (such as arsenic, beryllium, cadmium)
- Having radiotherapy before
- Air pollution
- Family history
Lung Cancer Symptoms
Obesity, sedentary life, malnutrition, smoking, and alcohol invite cancer. Lung cancer also, unfortunately, does not give early symptoms. Symptoms may not cause significant complaints until the disease is very advanced. The progression of cancer without symptoms is the most important factor that makes this cancer so dangerous.
- Chronic cough
- Coughing up blood (bleeding from the mouth)
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath,
- Bronchitis and Pneumonia
- Loss of Appetite
- Loss of Weight
- Hoarseness
- Chest, upper and middle back pain
- Swelling of the neck or face
Lung Cancer Treatment
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): The choice of treatment is related to the extent of the disease. In this group of cancers, surgical intervention is the most common form of treatment. Radiotherapy and chemotherapy are also used to slow down the duration of the disease and control the symptoms.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC): In many cases, the disease has spread to other parts of the body when diagnosed. Therefore, surgical treatment is rarely performed in small cell lung cancer. Doctors often prefer chemotherapy to reach cancer cells that have spread throughout the body. Treatment involving chemotherapy may also be administered by targeting cancers in the lungs or cancers in other parts of the body. Radiotherapy for the brain can be applied in some patients., even if there is no cancer there. This is done for preventing cancer (tumor) in the brain.
Quit Smoking!

Smoking is the most common risk factor for the development of lung cancer. Lung cancer should be a preventable public health problem as eighty-five percent of patients have direct tobacco exposure. In order to prevent lung cancer, which is a preventable disease, you should stop smoking first. Stopping smoking reduces your risk of getting lung cancer approximately fifty percent after ten years.